A Quick Guide to Codeless Software
Codeless web development software removes the need for manual coding of software apps and, in doing so, cuts the time and cost of software development by as much as 60%.
Codeless Software – A Definition
Codeless software is a short-form term to describe a software development approach that removes the visibility of software code from screens when programming software applications. An abstraction layer is used to create applications logic, data structures and forms using software wizards and building blocks. While No-Code platforms allow software developers to quickly build applications by a simple drag-and-drop tool, codeless software goes a step further by eradicating visibility of software code in the software development and publishing journey.
This new form of rapid application development software is today frequently used in web development and enterprise computing. Normally, Low Code and No-Code app development platforms used for codeless authoring are deployed on a cloud computing environment. They help organizations to bring new software applications to market faster, and at a lower cost.
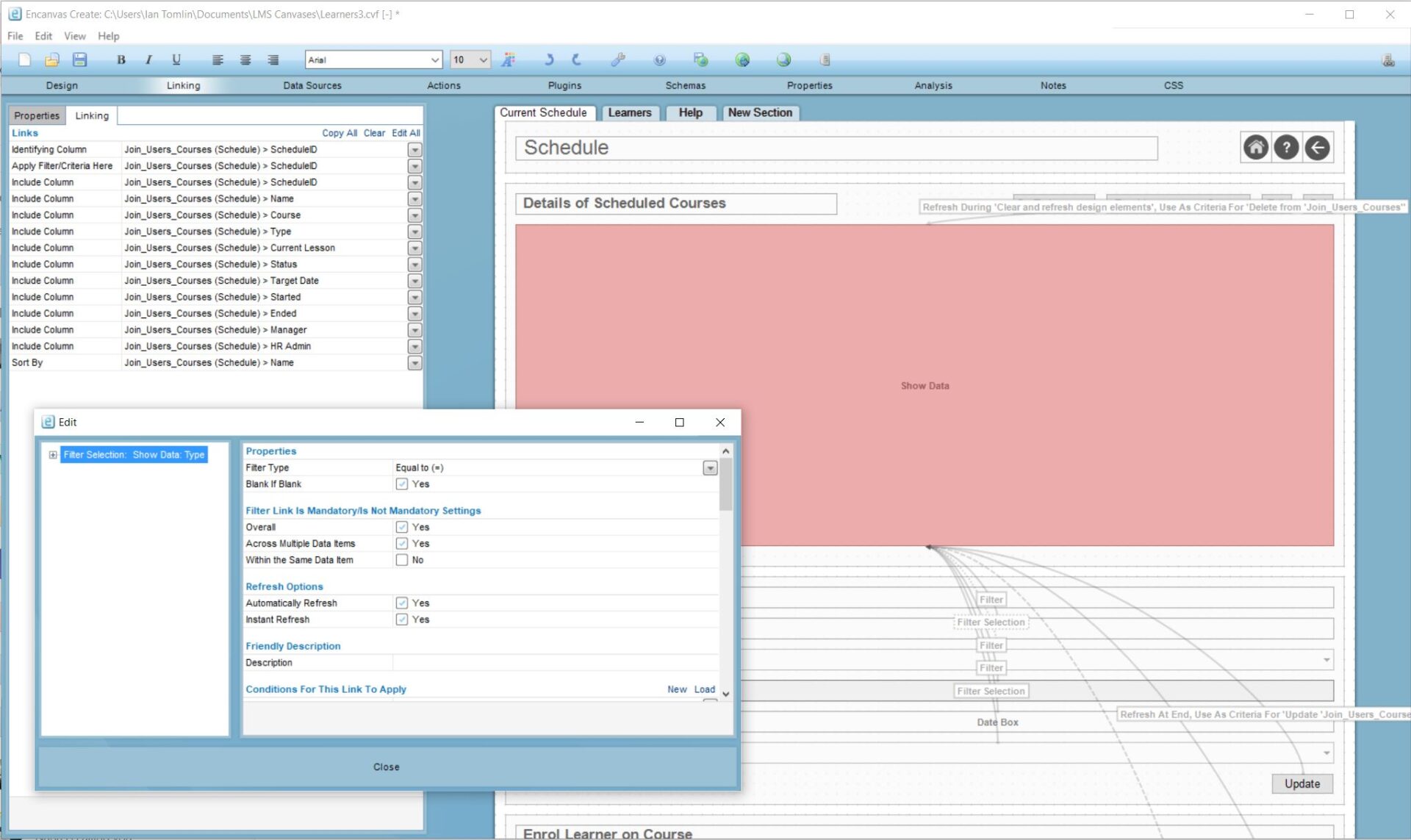
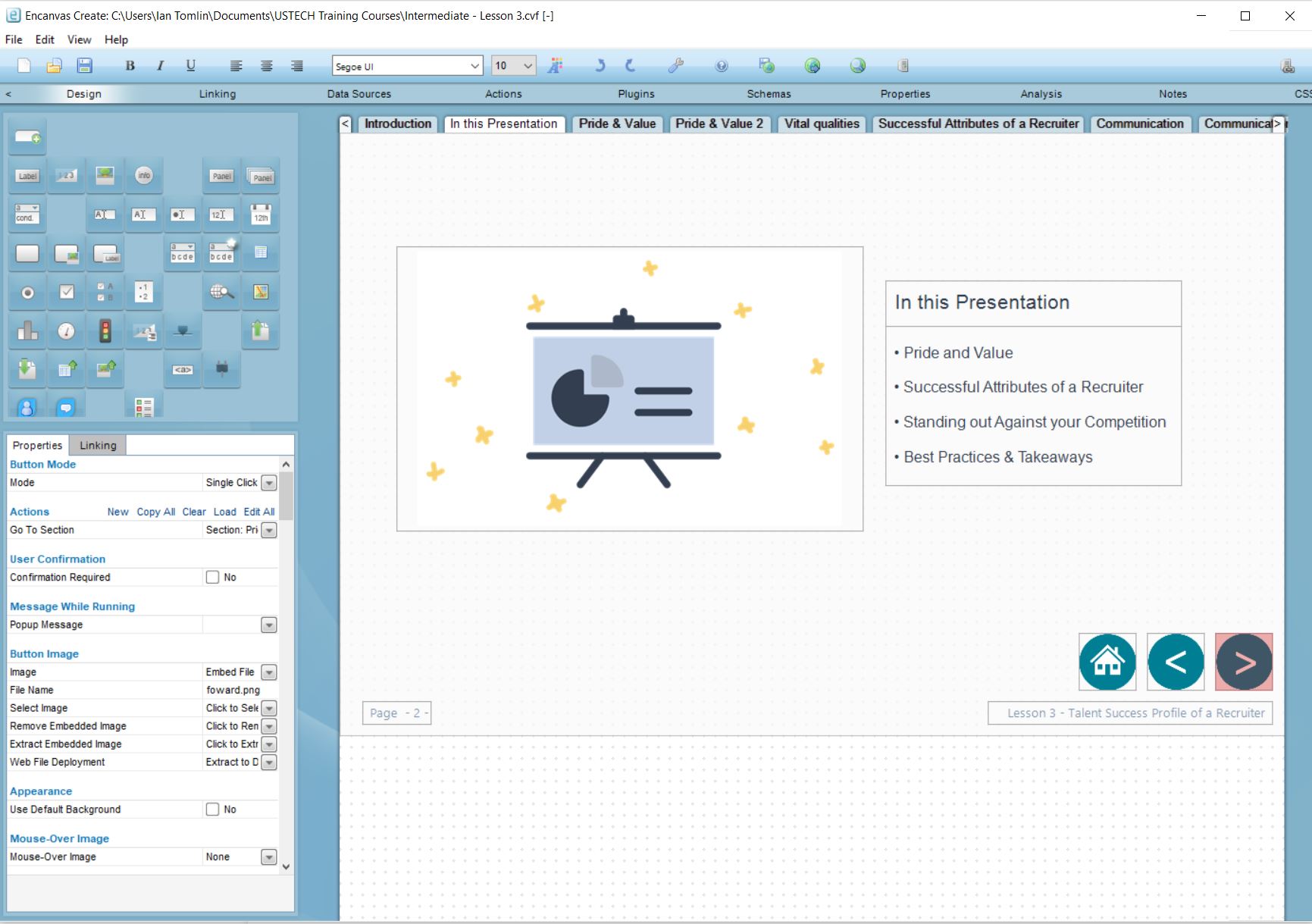
Examples of codeless web deveopment screens (copyright Encanvas 2022). Note the absence of any visible code.
The need for adaptive IT to support digital transformation
Markets have always been competitive, but with the progressive rise of digital business and the globalization of markets, the very structure of markets is changing too. It means that organizations must find faster and smarter ways to adapt their enterprise computing platforms to maximize customer value and minimize spend. It’s not just people and processes, but technology too is having to adapt faster and more often to change.
This means traditional IT platforms are being displaced by Low Code or Codeless enterprise software application platforms that are designed to adapt to change constantly, and offer productivity enabling tooling to serve the needs of change managers orchestrating change.
How organizational change has changed
At one time, an organizational change was a rare thing. Business models rarely altered and the structure of organizations – i.e. how organizational structures were designed and resourced – had no need to change. Once people were assigned roles in the organization, they rarely moved beyond their role or department. Not today. The business models organizations operate are changing frequently and rapidly.
This is because, in a digital age, the structure of markets and the nature of competition. Many new forms of competition emerge from beyond the traditional players in any given market. We are seeing retailers selling holidays, telecoms contracts and financial services products, utilities and automotive manufacturers selling data and online retailers selling everything! In such a tumultuous market for products and services, suppliers have to respond to change faster. This means organizations are facing near constant organizational restructuring.
The need for adaptive IT to support digital transformation
Markets have always been competitive, but with the progressive rise of digital business and the globalization of markets, the very structure of markets is changing too. It means that organizations must find faster and smarter ways to adapt their enterprise computing platforms to maximize customer value and minimize spend. It’s not just people and processes, but technology too is having to adapt faster and more often to change.
This means traditional IT platforms are being displaced by Low Code or Codeless enterprise software application platforms that are designed to adapt to change constantly, and offer productivity enabling tooling to serve the needs of change managers orchestrating change.
Breaking down the barrier between IT and the business
Codeless software development is a major breakthrough in the evolution of enterprise computing because, until its arrival, enterprise-grade applications were largely created by expert software development teams in back-offices, working ‘offline’ as opposed to developments carried out in near-real-time in workshops.
Evidence shows that users and stakeholders of applications are very much put off by the visual presence of code and script on computer screens as it’s a language they simply don’t understand. In consequence, they feel isolated and unqualified to present their case for enhancements to applications designs during review meetings; some claiming they feel awkward presenting ideas for improvements because of concerns over the amount of extra work they might be placing on IT colleagues.
A professional development tool-set for citizen developers
Codeless web development software is sponsoring a new talent market, as non IT professionals can enter into a career of developing professional applications.
Examples of mobile and web desktop applications developed using codeless programming
The rise of the citizen developer
The last decade has seen the gradual erosion of centralized IT power in technology selection and decision making. This is partly because departmental leaders have grown more confident in their appreciation of technology and its potential to automate their processes. It is also because read-to-deploy Business Intelligence, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications and robotic process automation (RPA) tools have made it possible for departmental managers to request software tooling that instantly works to address task fulfilment challenges.
During the period, the term ‘citizen developer’ has arrived in enterprise software development vernacular. A Citizen Developer is someone who wants to author an application but lacks IT expertise (particularly coding or scripting) and tools. A wave of Low-Code and Codeless software applications have evolve to aid citizen developers in their quest to use software applications to solve their individual or team productivity challenges.
Codeless software applications development and the citizen developer
Codeless web development software platforms equip citizen developers with the tools they need to design applications without coding or scripting, to then deploy apps using one-click deployment methods.
This latest genre of technology raises the bar on what can be achieved by citizen developers. Toolkits enable non-programmers to build complete end-to-end business applications, deploy them, and manage them. This means enterprise-grade apps can be designed and deployed by non-IT people without compromizing IT governance and security.
For some individuals, citizen development codeless software offers the potential of a new career by offering services to businesses through task portals live Fiverr and TopTemp to build apps without coding.
The risks and rewards of investing in codeless software development tools
Codeless software has endured a challenging evolution to gain credibility for being useful and professional. In this section, we look at the pro’s and con’s of adopting codeless app development methods.

PROs
The benefits of codeless applications development
Sited benefits of using Codeless applications development platforms include:
- Faster time to market of new apps
- Lower development costs and risks
- Higher quality apps – because designers are better equipped to understand and apply the needs of users, stakeholders and the business
- Improved data management and governance controls
- Better data security because use of shadow data is removed from the enterprise
- Capacity is released from IT teams who no longer need to directly support software developments, so they can concentrate on more expert activities demanding their skills
CONs
The risks
Adoption of Low-Code and Codeless applications development software used to be seen as a high-risk venture. IT teams were concerned about a loss of influence, control and governance over deployed systems. Fortunately, modern enterprise applications software platforms carefully balance the needs of citizen developers with the expectations of IT teams, so everyone gains. Deployed applications bring MORE INFLUENCE, CONTROL AND GOVERNANCE to IT teams, not less. This is because:
• They are able to respond to the long-tail of demand from departments for new situational applications; removing calls for two-speed IT solutions and dedicated ‘rapid development’ DevOps teams.
• Use of ‘enterprise-grade’ applications development tools removes the existence of self-authored applications such as spreadsheets (so-called ‘shadow systems’ because their existence is unknown to IT teams).
• Furthermore, it means any created data becomes visible to IT and data security governance professionals rather than being held by users on local hard-drives (so-called ‘shadow data’).

About Ian Tomlin
Ian Tomlin is a management consultant and strategist specializing in helping organizational leadership teams to grow by telling their story, designing and orchestrating their business models, and making conversation with customers and communities. He serves on the management team of Encanvas and works as a virtual CMO and board adviser for tech companies in Europe, America and Canada. He can be contacted via his LinkedIn profile or follow him on Twitter.
Now read:

